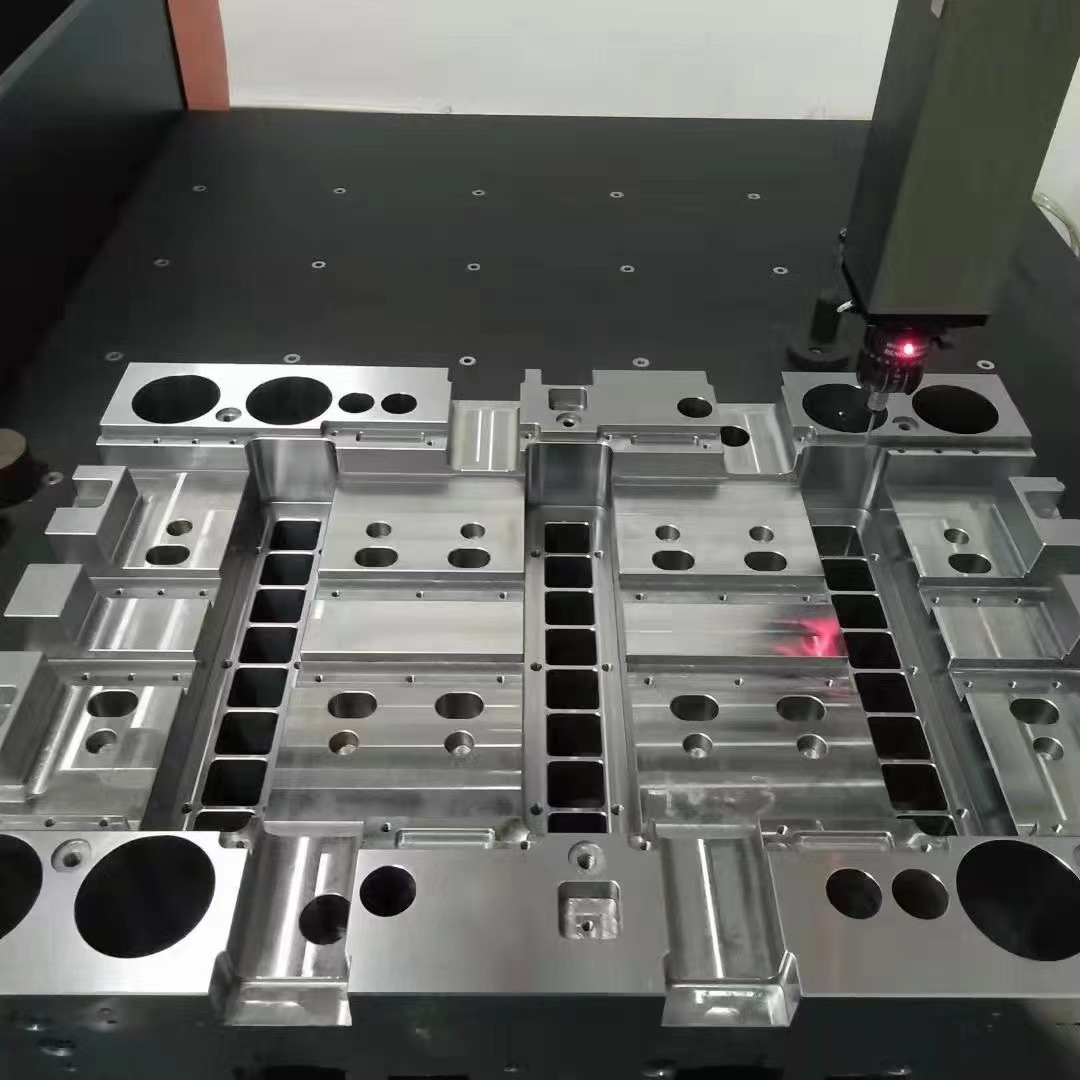
Mold bases play a crucial role in the manufacturing industry, especially in processes such as injection molding and die casting. Understanding the various components and functions of mold bases is essential for manufacturers looking to optimize their production processes. This article delves into the meaning of mold bases in manufacturing, their types, materials used, and their significance in producing high-quality products.
What is a Mold Base?
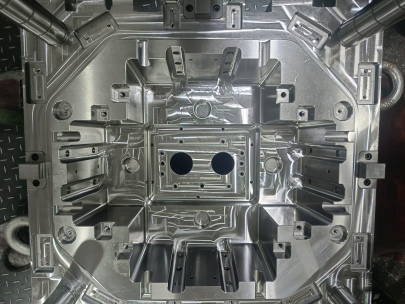
A mold base is a fundamental structure that houses the components of a mold, providing the necessary support and framework to facilitate the molding process. The mold base acts as the foundation upon which the mold plates, inserts, and other critical elements are mounted. It is designed to withstand high pressures and repetitive cycles during the injection molding process.
Components of a Mold Base
A typical mold base consists of several key components, each serving a specific purpose:
- Mold Plates: These include the cavity plate and core plate, which form the shape of the final product.
- Ejector System: This system helps to eject the molded part from the cavity after the molding cycle is complete.
- Guide Pins and Bushings: These components ensure proper alignment of the mold halves during closure.
- Cooling Channels: Channels are integrated within the mold base to allow for temperature regulation during the cooling phase.
- Locking Mechanism: This secures the mold halves together during operation to prevent any leakage of the molten material.
Types of Mold Bases
There are several types of mold bases available, each suited for different manufacturing applications:
| Type of Mold Base | Description | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Standard Mold Base | Commonly used in the industry, these bases are pre-made and widely available. | General plastic parts, automotive components. |
| Custom Mold Base | Designed specifically for unique applications, offering tailored solutions. | Specialized parts, intricate designs. |
| Multi-Cavity Mold Base | Allows for the production of multiple parts in a single cycle, increasing efficiency. | Consumer goods, packaging items. |
| Hot Runner Mold Base | Incorporates heated channels to keep the plastic molten as it moves to the mold cavity. | Thin-walled components, complex geometries. |
Materials Used in Mold Bases
The choice of materials for mold bases is crucial for ensuring durability, heat resistance, and performance. Common materials used include:
- Steel: Offers high strength and durability, suitable for various production cycles.
- Aluminum: Lightweight and provides excellent thermal conductivity, often used for low-volume runs.
- Stainless Steel: Corrosion-resistant, ideal for applications involving aggressive materials.
- Composite Materials: Combining plastics and metals for specific advantages, usually in specialized molds.
The Importance of Mold Bases in Manufacturing
Mold bases hold significant importance in the manufacturing process due to their impact on production efficiency and product quality. Here are some key points:
- Precision and Accuracy: Mold bases ensure that the molded parts are produced with high precision and consistent quality.
- Cost Efficiency: Using standardized mold bases can reduce production costs and lead times.
- Enhanced Productivity: Properly designed mold bases maximize the efficiency of the molding process.
- Longevity: Quality mold bases can withstand multiple production cycles without losing structural integrity.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Mold Bases
When selecting a mold base for a specific application, manufacturers should consider the following factors:
- Type of Material: Choose based on the specific requirements of the production process.
- Cavity Design: The complexity of the part geometry may require a custom mold base.
- Production Volume: High-volume production may benefit from multi-cavity molds.
- Budget Constraints: Evaluate the cost versus the expected output and longevity of the mold base.
- Maintenance Needs: Some mold bases require more maintenance than others; consider this in your decision-making.
Conclusion
Understanding mold bases is essential for manufacturers aiming to improve their production processes and product quality. As outlined in this article, mold bases serve as the backbone of the molding process, influencing everything from precision to cost efficiency. By taking the time to understand the various types, materials, and functions of mold bases, manufacturers can make informed decisions that lead to enhanced production outcomes and long-term success.
FAQ
What is the primary function of a mold base?
The primary function of a mold base is to provide the framework and support for the components of a mold, ensuring proper alignment and durability during the molding process.
What materials are commonly used in mold bases?
Common materials used in mold bases include steel, aluminum, stainless steel, and composite materials, each offering distinct advantages depending on the application.
How do mold bases affect production efficiency?
Mold bases impact production efficiency by ensuring proper alignment, enhancing cooling times, and allowing for multiple cavities, which together can significantly increase output.
Can mold bases be customized?
Yes, mold bases can be customized to meet the specific requirements of unique applications, including specialized geometries or materials needed for particular products.
What should be considered when maintaining mold bases?
When maintaining mold bases, manufacturers should consider regular inspections, cleaning procedures, and lubrication of moving parts to ensure longevity and performance.